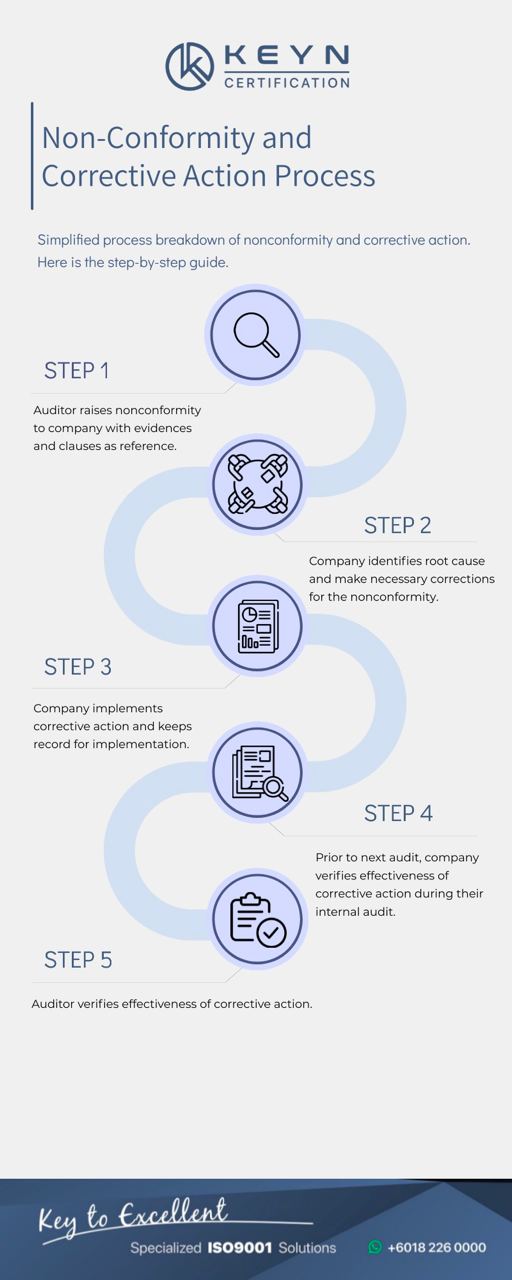
This infographic can help you understand how to resolve or close a Non-Conformance when you are raised with one by the auditor.
Step 1:
Auditor/Internal Auditor will raise Non-Conformance (NC) when the organization fails to comply or provide supporting documented information as proof of the practice. The NCs will be prepared in a Non-Conformance Report.
Step 2:
The audited organization should hold a management review to identify the root cause. Corrective actions are to be provided to auditor to address the consequences and NC. The corrective action has to include the target, person or department responsible with KPI to measure the outcome.
Step 3:
Organization implements the corrective action based on the approved corrective action by Auditor.
Step 4:
Organization conducts internal audit to compare the outcome of the implemented corrective action. Effectiveness is evaluated. If desired outcome is not achieved, corrective action will be redone with changes.If desired outcome is achieved, continual improvement has been made.
Step 5:
Auditor verifies the effectiveness of the implementation and approves for ISO certification.